Azure Search Extension
The Azure Search extension provides a search index manager and a search provider (it feeds an Azure Search index and retrieves search results).
- You need an Azure Search service to use the Azure Search provider.
- Azure Search can extract content from files (like PDFs, Word documents and other formats) which are stored in an Azure Blob Storage service.
For files which are stored elsewhere (not in Blob Storage), the Azure Search extension will try to convert them to text in order to generate vectors, but you may need a content conversion extension for some file types. The Nucleus built-in basic content converter can handle PDF and text formats.
If you just want to index file meta-data, along with your site content, you can use Azure Search without storing your files in Azure Blob Storage, but you won't get results when searching terms from within your file's contents.
How it works
Nucleus
The Nucleus search system is built to support a variety of search services. The Nucleus search system consists of:
- Search meta-data providers: Extensions and core components of Nucleus implement meta-data providers, which provide data to the search indexing system. The core includes meta-data providers for site pages and files, and modules (like Documents and Forums) also publish their data by implementing their own meta-data providers.
- Search index managers: Search extensions may implement a search index manager in order to populate an index. All configured search index managers receive all data from meta-data providers, and use meta-data to populate their index. Some search extensions (like a Google custom search) don't have a search index manager and just provide a search provider.
- Search providers: Search providers are called by the search module (and from other Nucleus components and extensions) to retrieve search results from an index.
- The Search Module presents a search user interface so that users can perform a search, and view results.
- The search feeder scheduled task runs periodically. It calls all meta-data providers and passes their data to all search index managers.
The Azure Search extension provides a search index manager and a search provider, so it can populate your Azure Search index, and query it for search results. The settings page provides a user interface to create and manage your search Azure Search index settings and Azure Search indexers, data sources and skill sets.
Make sure to check pricing for Azure services before enabling them. Microsoft charges extra for semantic ranking (pricing) and AI services (pricing) in addition to your Azure Search service.
Azure Search
The Azure Search index feed process consists of two parts:
- The "push" feed (search index manager) which runs on your web server, and populates the Azure Search index with content from Nucleus. File meta-data is
saved in your index by the "push" feed. File content can be extract if you have a content conversion extension which can handle the relevant file type.
The Nucleus core Basic Content Converter can handle HTML, Markdown and PDF formats, and text files are included in the index by the "push" feed because they don't need conversion. - The "pull" feed - which is one or more Azure Search Indexers - extracts document
content from files stored in your Azure Blob Storage service. The indexer runs in Azure and supplements the data in your index with content from within
your files. Indexers are executed automatically during the "push" feed process.
It doesn't matter what order the "push" and "pull" feeds run in, as they each update different fields in the index, but your content won't be searchable until the "push" feed has run, because the meta-data that is populated in the index is required by the search module.
The Azure Search extension settings are accessed in the Manage control panel.
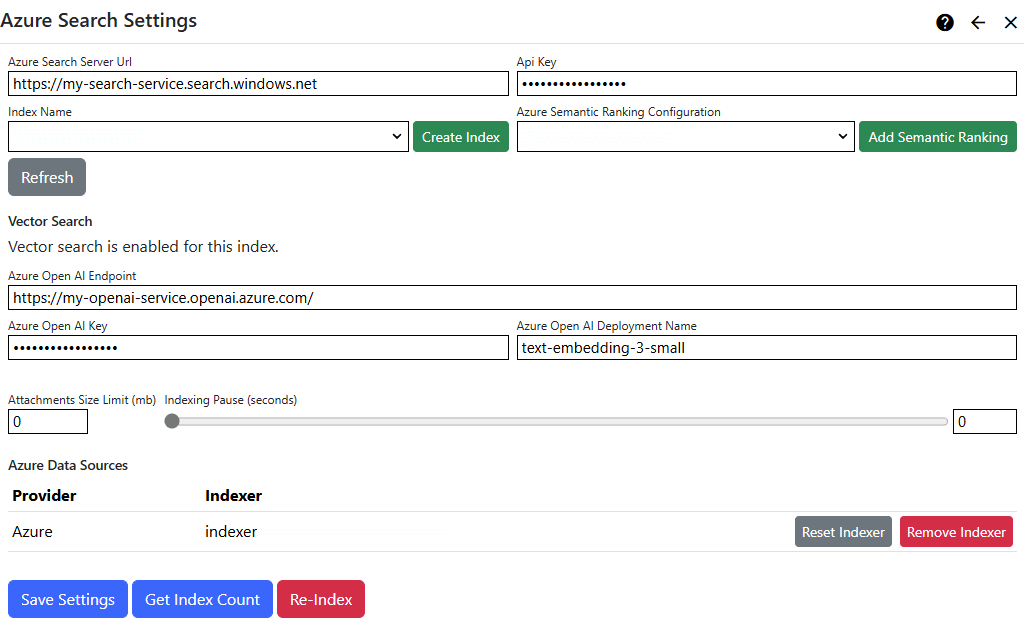
Settings
| Azure Search Server Endpoint | Enter the address of your Azure Search service, including the scheme (http: or https:). The Azure Search service endpoint is displayed in the Azure Portal/Azure Search/Overview page. |
| Api Key | Enter your Azure Search service API key. You can get your API key from the Azure Portal/Azure Search/Settings/Keys page. |
| Index Name | Select an index name. |
| - Create Index | Create a new index: Index names must be lower case, can contain only letters, numbers, dashes and underscores and must be 2-128 characters. |
| Azure Semantic Ranking Configuration | If specified, the selected Semantic Ranking Configuration is used when performing a search. |
| - Create Semantic Ranking Configuration | Create a new Semantic Ranking Configuration and enable semantic ranking. |
| Vector Search | Vector search is not enabled by default, because it uses Azure OpenAI, which must be set up separately and is charged by Microsoft based on usage. |
| - Azure OpenAI Endpoint | Enter the address of your Azure OpenAI service, including the scheme (http: or https:). Your Azure OpenAI service endpoint is displayed when you click "Click here to view endpoints" in the Azure Portal/OpenAI/Overview page or in Azure OpenAI studio. |
| - Azure OpenAI API Key | Enter your Azure OpenAI service API key. Your Azure OpenAI service keys are displayed when you click "Click here to view endpoints" in the Azure Portal/OpenAI/Overview page or in Azure OpenAI studio. |
| - Azure OpenAI Deployment Name | Enter your Azure OpenAI service embeddings model deployment name. Azure OpenAI model deployments are set up in Azure OpenAI studio. |
| Enable Vector Search | Click "Enable Vector Search" to enable and configure vector search for your index. |
| Attachments Size Limit | You can specify an upper size limit (in mb) for documents which are submitted to the index. Documents which are larger than the size limit will have index entries containing meta-data only. To specify no limit, enter zero (0). |
| Indexing Pause | You can specify an pause in-between each indexing operation (in seconds), or zero for no pause. See additional information below. |
Indexing Pause
The indexing pause is used to reduce the load on your server during search feed processing. In some hosting environments, the search feed can exhaust memory, processor or TCP connection limits.
Pausing in-between submitting each index entry gives the server time to free up resources. This setting makes your search feed take longer to run, but can prevent it from failing. If you are hosting in an Azure App Service, this setting is important, as Azure automatically stops and restarts applications which have too many TCP ports open.
If you are hosting in an Azure App Service, try an indexing pause of 2.5 seconds. This will reduce the number of HTTP requests to 24 per minute, which gives the Azure time to release unused SNAT ports. For a search index with 5000 entries, this would increase the search feed duration to around 3.5 hours.
Azure Data Sources
Your Azure file system providers are listed automatically.
| Add Indexer | Use the Add Indexer button to automatically create an indexer, data source and skill set for your Azure Storage files. |
| Remove Indexer | Use the Remove Indexer button to remove your previously-created indexer and data source. If you remove the last indexer that uses your skill set, it is also removed. |
| Reset Indexer | Use the Reset Indexer button to delete indexing tracking data from Azure Search. This triggers a full re-index the next time that indexing runs. |
Tools
| Get Index Count | Displays the number of entries in the index, for use when troubleshooting or verifying that your server is functioning correctly. |
| Re-Index | Use the Re-Index function to remove search indexing history to trigger full indexing the next time that the Search Feed scheduled task runs. |
Scoring Profiles: The Azure Search extension automatically creates a scoring profile for your index in Azure and sets it as the default. Refer to the Microsoft documentation for Scoring Profiles for more information.
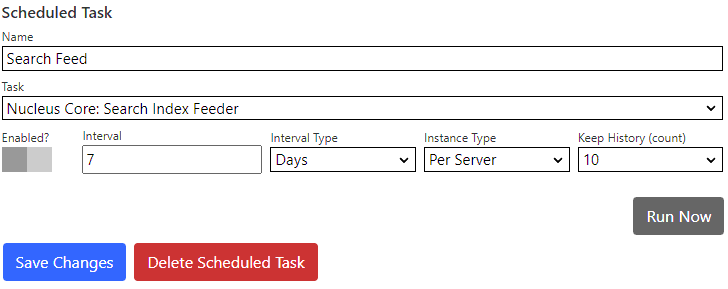
Search Feeder Scheduled Task
Nucleus has a built-in Scheduled Task which collects data from all installed search meta-data providers, and submits that data to all installed search index managers. You must create and enable the scheduled task in the
Settings/Schedulercontrol panel as it is not enabled by default.
Supported Capabilities
The Azure Search provider supports all of the capabilities of the Nucleus Search Module.
| Capability | Supported? |
|---|---|
| Search Suggestions | Yes |
| Filter By Scope | Yes |
| Maximum Page Size | 250 |
| Meta-data Display | |
| - Categories | Yes |
| - Result Score | Yes |
| - Size | Yes |
| - Published Date | Yes |
| - Resource Type | Yes |
| - Matched Terms Highlighting | Yes |
| Clear Index | No |
